|
|
|
|
 |
The setup for knurling can be made between centres or mounted in a solid chuck. Never attempt to knurl by holding the work in a rubber or metal Collet chuck, since the great pressures of knurling could damage these devices. It is important to support the work while knurling. If mounting the work between centres, make the centre holes as large as possible to allow for the strongest hold. If using a chuck to hold the work, use the tailstock centre to support the end of the work. If doing a long knurl, use a steady rest to support the work and keep the piece from springing away from the tool.
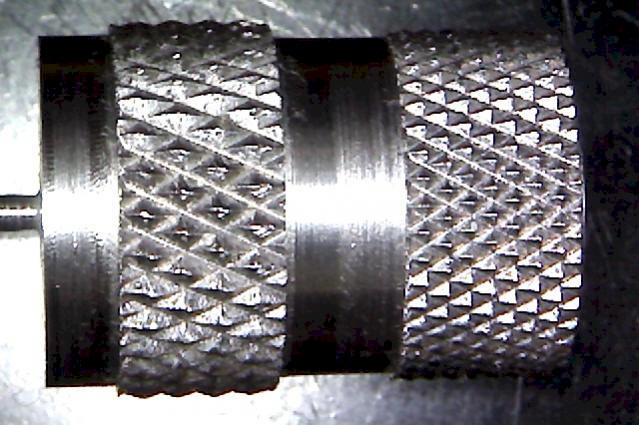
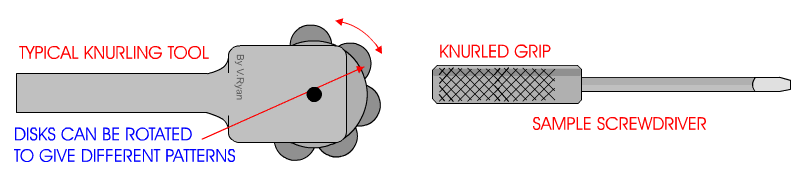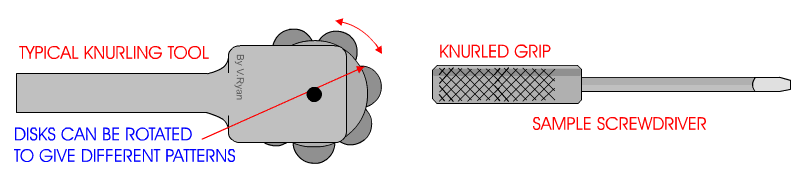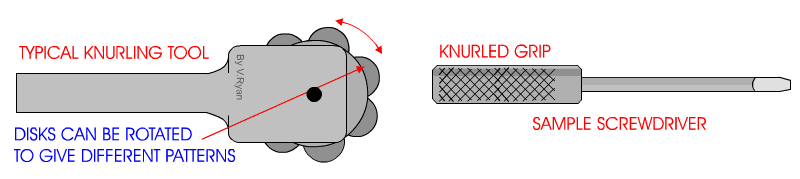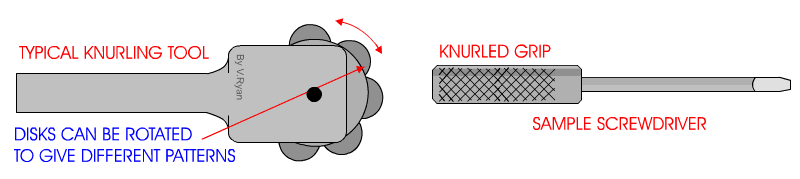
The knurling tool can be designed differently, but all accomplish the same operation. Two common types of knurling tools are the knuckle joint and revolving head type of knurling tools. The knuckle joint type is equipped with a single pair of rollers that revolve with the work as it is being knurled. The revolving head type of tool is fitted with three pairs of rollers so that the pitch can be changed to a different knurl without having to change the setup. There are two knurl patterns, diamond and straight.
There are three pitches of
rollers, coarse, medium, and fine.
The diamond is the most common pattern and the medium pitch
is used most often. The coarse pitch is used for
large-diameter work; the fine pitch is used for
small-diameter work.
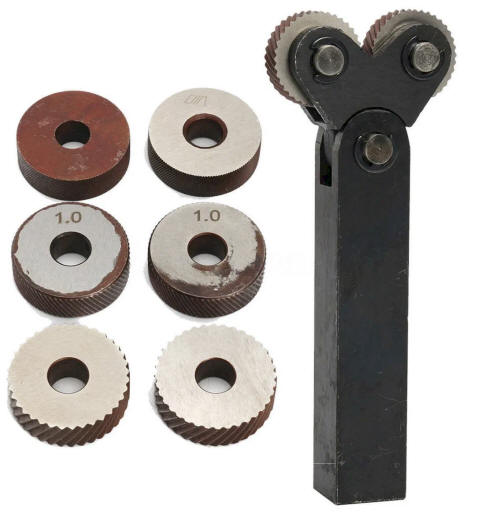 Knuckle joint knurling tool |
 Revolving head knurling tool |
 |
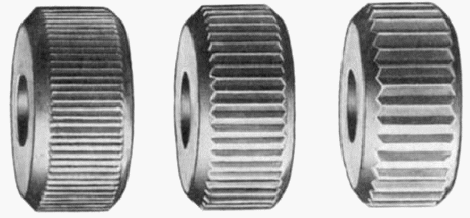 |
| Diamond pattern - Fine, Medium and Course | Straight pattern - Fine, Medium and Course |
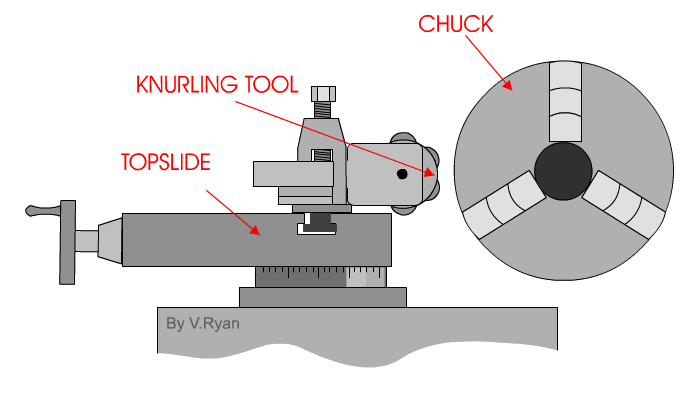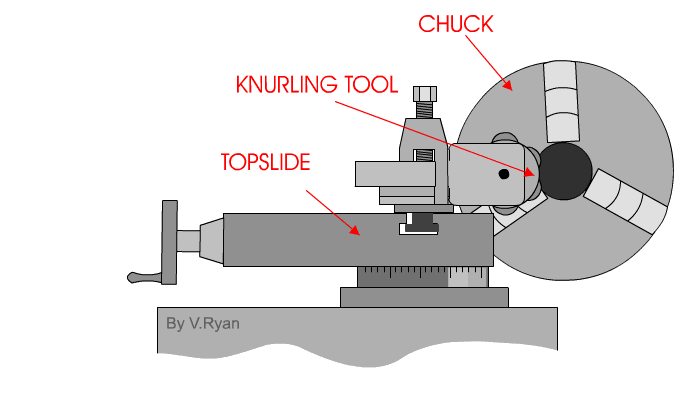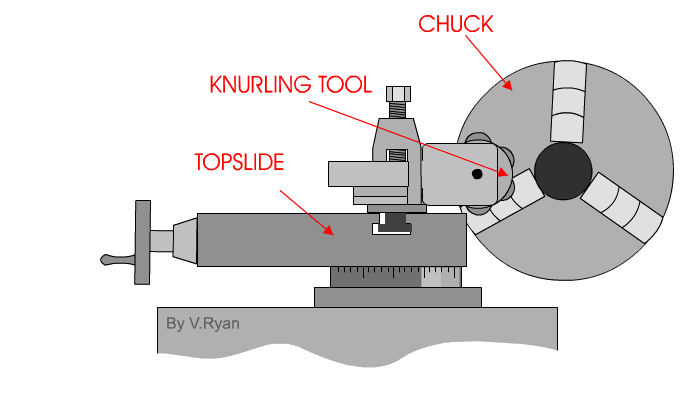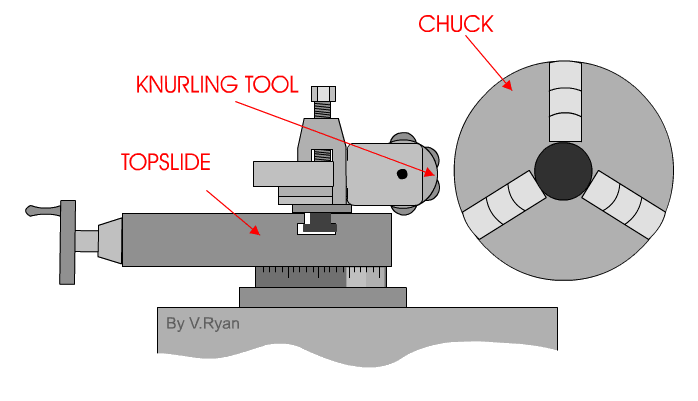
The knurling operation is started by determining the location and length of the knurl, and then setting the machine for knurling. A slow speed is needed with a medium feed. Commonly, the speed is set to 60 to 80 RPM, while the feed is best from 0.04 mm to 0.08 mm revolution of the spindle. The knurling tool must be set in the tool post with the axis of the knurling head at centre height and the face of the knurls parallel with the work surface. Check that the rollers move freely and are in good cutting condition; then oil the knurling tool cutting wheels where they contact the workpiece. Bring the cutting wheels (rollers) up to the surface of the work with approximately 1/2 of the face of the roller in contact with the work.
If the face of the roller is placed in this manner, the initial pressure that is required to start the knurl will be lessened and the knurl may cut smoother. Apply oil generously over the area to be knurled. Start the lathe while forcing the knurls into the work about 0.05 mm. As the impression starts to form, engage the carriage feed lever. Observe the knurl for a few revolutions and shut off the machine. Check to see that the knurl is tracking properly, and that it is not on a "double track"
Never stop the carriage while the tool is in contact with the work and the work is still revolving as this will cause wear rings on the work surface . Check the operation to ensure that the knurling tool is not forcing the work from the centre hole. Keep the work and knurling tool well oiled during the operation. Never allow a brush or rag to come between the rollers and the work or the knurl will be ruined.
|
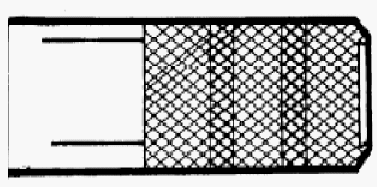
Wear rings as a result of stopping on the work |
Incorrect impression |
Correct impression |
Reset the tool if needed; otherwise, move the carriage and
tool back to the starting point and lightly bring the tool
back into the previously knurled portion. The rollers will
align themselves with the knurled impressions. Force the
knurling tool into the work to a depth of about .15 mm
and simultaneously engage the carriage to feed toward the
headstock. Observe the knurling action and allow the tool to
knurl to within .3 of the desired end of cut, and
disengage the feed. Hand feed to the point where only
one-half of the knurling wheel is off the work, change the
feed direction toward the tailstock and force the tool
deeper into the work.
Engage the carriage feed and cut back to the starting point.
Stop the lathe and check the knurl for completeness. Never
allow the knurling tool to feed entirely off the end of the
work, or it could cause damage to the work or lathe centres.
The knurl is complete when the diamond shape ( or straight
knurl) is fully developed. Excessive knurling after the
knurl has formed will wear off the full knurl and ruin the
work diameter. Move the tool away from the work as the
centres. The knurl is complete when the diamond shape (or
work revolves and shut off the lathe. Clean the knurl with a
brush and then remove any burrs with a file.