3.2 Demonstrate an understanding of screw-threads.
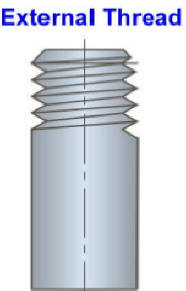
External Thread
A external thread is defined as a ridged uniform section in the form of a helix on the external surface of a cylinder. Examples are bolts.
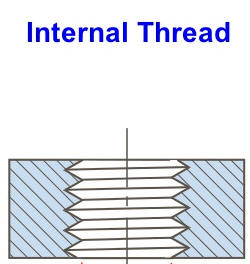
A internal thread is defined as a ridged uniform section in the form of a helix on the internal surface of a cylindrical hole. Examples are nuts.
-
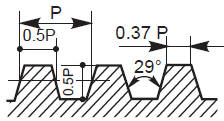
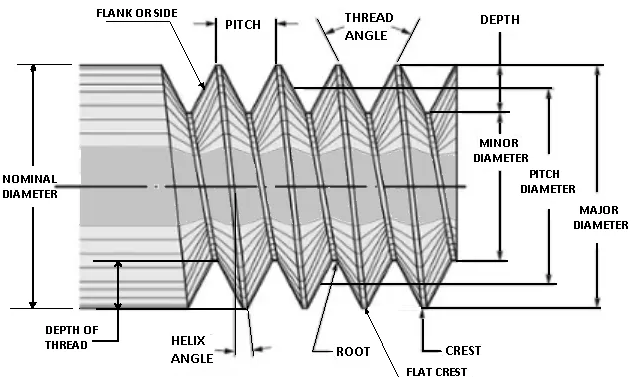
The pitch diameter (often called the effective diameter) of a parallel thread is the diameter of the imaginary co-axial cylinder which intersects the surface of the thread in such a manner that the intercept on a generator of the cylinder, between the points where it meets the opposite flanks of a thread groove, is equal to half the nominal pitch of the thread.
-
The major diameter of a thread is the diameter of the imaginary co-axial cylinder that just touches the crest of an external thread or the root of an internal thread.
-
The minor diameter is the diameter of an imaginary cylinder that just touches the roots of an external thread and (or) the crests of an internal thread.
-
The crest of a thread is the prominent part of a thread, whether internal or external.
-
The root is the bottom of the groove between the two flanking surfaces of the thread whether internal or external.
-
The flanks of a thread are the straight sides that connect the crest and the root.
-
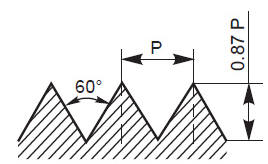
The thread angle of a thread is the angle between the flanks, measured in an axial plane section.
-
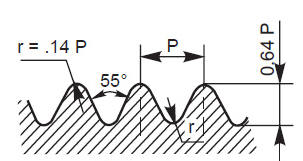
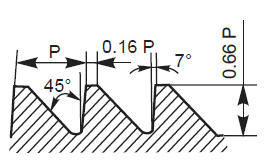
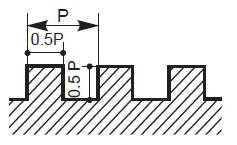
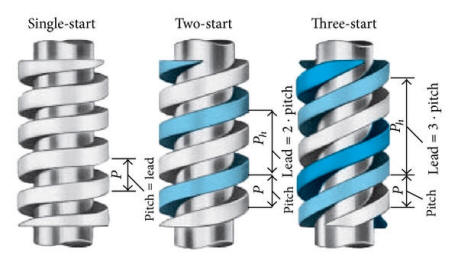
The pitch of a thread is the distance, measured parallel to its axis, between corresponding points on adjacent surfaces, in the same axial plane.
-
The terms lead angle or helix angle are the same. The helix angle is the angle between the helix of the thread and a line parallel to the axis of rotation
-
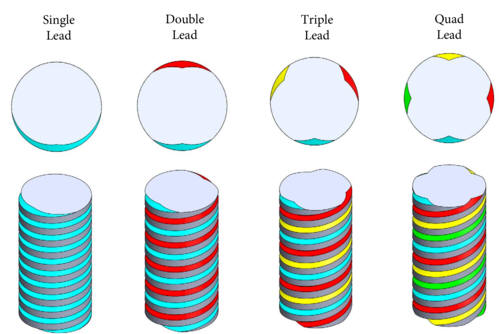
The lead is the axial advance of a helix or screw during one complete turn (360°) The lead for a screw thread is the axial travel for a single revolution