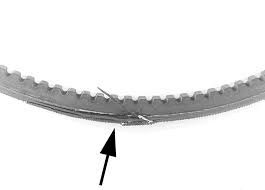
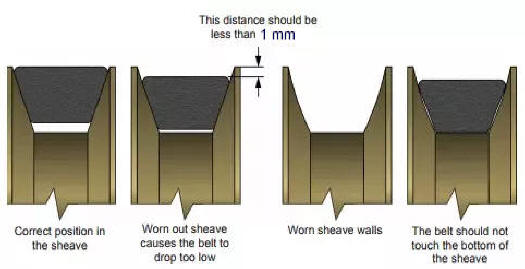
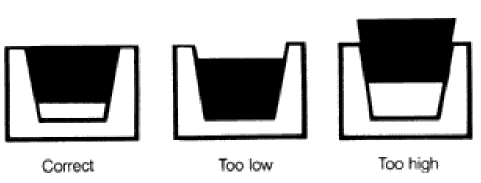
|
  |
Most plants will have maintenance planers. They will keep a record of all plant machines including belt drives. These records will include the following on a belt drive:
- When was the drive installed
- When was it last inspected
- Who did the inspection
- What parts where replaced
- All drawings and manufacturing manuals will be kept by planner
The maintenance planner will also prepare the following documents for the maintenance fitter:
- Job cards will be prepared by the maintenance planner
- Plant shutdown permission permit will be obtained
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Straight Edge |
Various tools | Torque wrench | Browning tension device | Laser pulley aligner |