| Type of Gears - Rack
and Pinion |
|
Video |
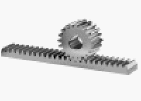
| Rack and pinion gears
are a mechanical system that converts rotational motion into linear
motion (or vice versa) using a circular gear (pinion) that meshes with a
flat, toothed bar (rack). They are widely used in applications requiring
controlled and precise linear movement |
| |
| Key features and
advantages: |
- Simplicity and
compact design: They are a straightforward and compact way to
convert rotational to linear motion, resulting in lower weight and
fewer parts.
- High efficiency: The
direct-contact design provides efficient power transmission.
Low friction: They have reduced friction compared to other systems,
which improves efficiency.
- Precise and direct
feedback: The system offers a high degree of precision and gives the
user more direct feedback, which is beneficial for steering
applications.
- Cost-effective:
Their simple design makes them easy to manufacture and
cost-effective.
- Long lifespan: With
proper maintenance and lubrication, they can have a long operational
life.
|
| Disadvantages: |
- Limited load
capacity: They are not as strong as other systems and may be
unsuitable for heavy-duty applications due to their limited
load-carrying capacity.
- Backlash: Some
systems can suffer from backlash, which is a small amount of play
between the gear teeth.
- Vulnerability: The
exposed design can make the components vulnerable to damage from
road debris or contamination.
- Noise: They can be
noisier than some other gear systems, which may affect the driving
experience in vehicles.
- Wear and tear: The
constant meshing of gears can lead to wear over time, requiring
proper lubrication and maintenance to prevent excessive wear.
|
| How they work |
-
Rotational Input to Linear Motion: When the pinion gear, attached to
a rotating shaft (like a steering column), turns, its teeth engage
with the teeth on the stationary or movable rack. This engagement
forces the rack to move in a straight line.
-
Linear Input to Rotational Motion: Conversely, if the rack is moved
linearly by an external force, it causes the pinion gear to rotate.
- The
speed of the rack's movement depends on the diameter and rotational
speed of the pinion.
|
| Materials and
applications |
- Materials: They are
made from various materials, including plastic (like acetal or
nylon) and metals (like aluminum, brass, and stainless steel)
- Applications: They are
widely used in industries such as automotive, manufacturing, and
consumer electronics.
Plastic gears: These are lightweight, non-rusting, and can
operate without lubrication, making them suitable for food
production and medical equipment.
- Metal gears: These
offer greater strength, load-carrying capacity, and heat
resistance.
|
|
|