| Cutting tool
terminology |
|
Video |
| The cutting tool is the
key element in machining where metal removal is required for whatsoever
reason. For best output and optimum performance with minimum efforts and
work input, the cutting tool is designed in a specific way. There are
various terms associated with the design of the cutting tool. Here is
cutting tool terminology with detailed explanation. |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
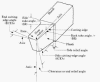
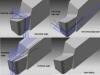
Back rack angle |
- In cutting tool
terminology, it is the angle between the line parallel to the tool
axis passing through the tip and the rack face.
- The angle is
measured in a plane perpendicular to the base
- For brass, back rack
angle will be zero.
- Positive back rack
angle is used for soft and ductile material while negative back rack
angle is used for hard and brittle material.
|
|
Side cutting edge angle |
- It is the angle
between side cutting edge and the line extending the shank.
- The angle is
measured in the plane perpendicular to the base.
- Feed represents
uncut chip thickness
- The depth of cut
represents the width of the chip.
|
| Side rack angle |
- It is the angle
between the rack face and the line passing through the tip
perpendicular to the tool axis.
- The angle is
measured in a plane perpendicular to the base
- Value of the angle
varies from 5 to 15
- Large positive rack
angle results in less chip formation, less cutting force, good
surface finish and low heat dissipation rate.
|
| Side relief angle |
- It is the angle
between the side flank and the line passing through the tip
perpendicular to the base.
- The angle is
measured in a plane perpendicular to the tool axis.
- Value of the angle
varies from 5 to 15
- Side relief angle is
provided to prevent side rubbing after elastic recovery of the
workpiece
|
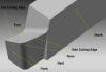
| End cutting edge
angle |
- It is the angle
between the end cutting edge and the line passing through the tip
perpendicular to the tool axis.
The angle is measured in a plane parallel to the base.
- Value of the angle
varies from 8 to 15
- Small end cutting
edge angle results in tool chatter
|
| End relief angle or
clearance angle |
- It is the angle
between nth e end flank and the line passing through tip
perpendicular to the base
- The angle is
measured in plane parallel to the tool axis
- In the ductile
material large end relief angle is provided due to more elastic
recovery
|
| Nose radius |
- Nose radius provides
long tool life and good surface finish.
- Large nose radius
results in more power consumption.
|
| |