| Flooded and suction
head |
| |
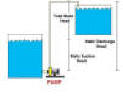
| Flooded suction
and suction head refer to the
position of the pump in relation to the fluid it is pumping: |
| |
| Flooded suction |
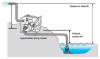
| A flooded suction pump
is designed to work by being gravity-fed the fluid that is to be pumped.
This type of pump does not require a method of priming the fluid. There
are numerous types of flooded suction pumps. A flood suction pump
application is unlike a submersible pump application. In a flooded
suction pump application, the pump and the pump motor are located
outside of the fluid to be pumped. Whereas, in a submersible pump
application the pump and the pump motor are located inside of the fluid
that is to be pumped. |
|
|
| |
| Advantages of Flooded Suction Pumps: |
- The flooded suction
pump offers several major advantages over other types of pumps:
- Priming: They don’t
have to be primed. They are automatically primed because the fluid
they will be pumping is gravity fed directly into the pump, always
keeping it primed.
- Efficiency: When a
pump is submerged there is positive fluid pressure at the inlet of
the pump. This condition can increase efficiency due to the less
energy required to move fluid through the liquid path of the pump.
- Maintenance &
Accessibility: When the pump is located outside of the fluid being
pumped, the pump can be easily accessible for routine maintenance. A
shut-off valve should be positioned before the inlet of the pump
which will allow the fluid to the pump to be shut off, then, the
pump can be easily removed from the application.
|
| Disadvantages to
contend with: |
- Potential to lose
Prime: If the slurry mixture is too thick or viscous, it may not
easily feed into the pump which can cause the pump to lose prime.
Thus, the mixture needs maintain adequate fluidity to constantly
feed the pump and prevent this from happening.
- Corrosion: Prolonged
exposure to a liquid of any sort will lead to corrosion. Submersible
pumps are often used to handle liquids that are corrosive and
abrasive. Seals are especially prone to corrosion, which leads to
leaks and damage to the motor. To counteract corrosion these pumps
need to be made of corrosion-resistant material, which can make them
more expensive than other types of pumps of the same capacity.
- Low level in feed
may cause a
coriolis
(swirl) effect that may cause the pump to suck in air, instead of
fluid.
- Wherever possible,
flooded suction pumps should be inspected as often as possible. In
this way, any necessary repairs can then be carried out to prolong
the life of the pump.
|
|
Suction head |
| With a suction head the
pump is above the fluid level. This pumping arrangement is
normally is the more problematic of the two arrangements. The pump
has to create a vacuum and maintain a vacuum in the suction side of the
pump to work. |
|
|
| Failures of pumps
with suction head: |
- Air leaking into
pump through pipe joints and mechanical seals, destroying negative
pressure to operate
- Block strainer
- Foot valve above
water level
- Foot valve faulty
- impeller blocked
- Impeller not
spinning fast enough
- Suction head to high
- Cavitation of pump
|
| |
| |