| Pumps curves
Videos |
|
When selecting a centrifugal
pump, one should match the performance of the pump to that needed by the
system. To do that, an engineer would refer to a pumps composite curve.
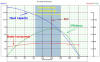
A typical composite curve includes the pump performance curves,
horsepower curves and NPSH required. A pump performance curve indicates
how a pump will perform in regards to pressure head and flow. A curve is
defined for a specific operating speed (rpm) and a specific inlet/outlet
diameter |
| |
| The ability to read pump
curves is essential to long-term pump performance. In new applications,
they aid in the selection of a pump that meets performance requirements.
In troubleshooting applications, they help engineers and operators
evaluate conditions and solve performance problems. |
| |
A pumps performance will
be inline with the pressure losses in the system, with pumps producing a
differential flow and pressure based on the conditions at the inlet. A
pump curve is a graphical representation of what flows and differential
pressures can be produced by a pump.
|
| As 90% of problems with
pumps are caused by the system they are installed in, it is important to
note that pump selection is just part of the process of selecting a pump
which is right for the process.
In order for a pump to be
selected for your process it is important that the following are known: |
- Fluid being pumped
- Application
- Flow Required
- Pressure required
- Viscosity of fluid &
Specific Gravity
- Temperature
- Power available /
Power medium being used to drive pump.
|
| Reading a
pump performance curve |
| In the simplest words,
pump performance curve is a graph of 'differential head' developed by
the pump, plotted against the operating flow rate.
When more fluid is pushed
through the pump, it is generally going to develop less differential
head (given the mechanical and power constraints)
|
| |
| |
| |
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U8iWNaDuUek |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
https://www.csidesigns.com/blog/articles/how-to-read-a-pump-curve |
|
|