- Make sure the pump unit is placed in such a manner that it is not subjected to any distorting forces.
- Make sure there is enough space around the pump unit for operation and maintenance.
- Make sure the top of the pump unit is not covered. This is important because the diesel engine driven pump unit draws in fresh air from the top.
- Make sure the front and sides of the pump unit are not covered. This is important because the diesel engine driven pump unit expels heat on these sides
- Select the diameter and length of the suction and pressure pipes as well as those of any additional components such that the inlet pressure remains above the minimum allowable value.
- The operating pressure must not exceed the maximum allowable value. The power rating of the installed drive system must be sufficient. NPSH graphs are available on request.
- The diameters of the
pipes must be equal to or greater than the connection sizes on the
pump.
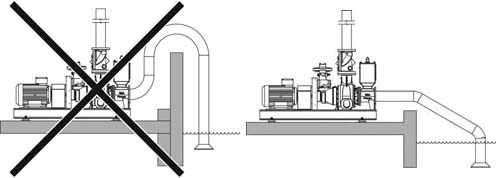
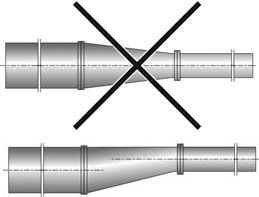
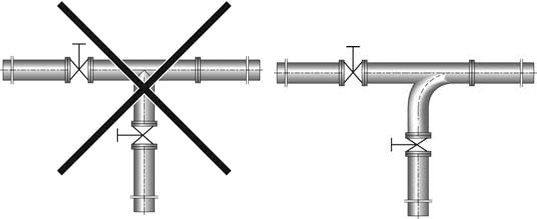
If possible, the transition between various pipe diameters must be made with a transition angle of approx. 8 degrees. - The pipe must be properly aligned with the pump connection.
- It must be possible to connect the flanges of the pipes and pump together without putting any of the parts under stress.
- In the case of
vibration and/or hot liquids, install expansion elements in the
pipes.
Support the pipes directly in front of the pump. The weight of the pipes and fittings may not be supported by the pump. - Install shut-off valves in the suction and pressure pipes as close as possible to the connection flanges in order to allow isolation of the pump for maintenance and repair work. The shut-off valves must be of a type that allows straight-line flow, such as gate or globe valves. The internal diameter of the shut-off valve must be the same as that of the pipe.
- If there is a possibility that a backflow of liquid could cause the pump to turn in the opposite direction when stopped, a non-return valve must be placed in the piping to prevent this.
- Install measurement instruments in the piping for monitoring during operation.
- If applicable, connect the pump unit to a suitable safety system. This is left to the judgement of the designer of the installation.
- Insulate or shield hot pipes.
- Observe specific regulations that pertain to the suction and pressure pipes.
- Thoroughly clean all parts that come into contact with the transported liquid before putting the pump unit in operation.
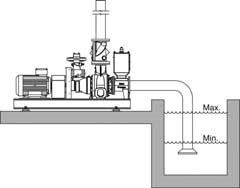
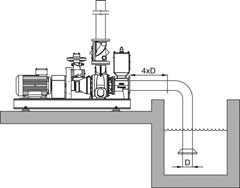
| Suction pipe | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
| In the case of self-priming pumps fitted with a separate suction bend, this bend must never be removed or rotated. | |
|
|
| Pressure pipe | |
|
|
|
WARNING Prevent sudden closure of the pressure pipe that would cause water hammer. |
|
|
|
|
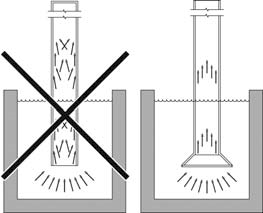
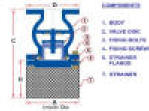
Suction strainer When pumping polluted liquid or liquid that may contain solid particles, install a suction strainer in the suction opening. |
|
|
|