| NPSH | Nett positive suction head – total head at pump suction branch over and above the vapour pressure of the liquid being pumped |
| NPSHr | NPSH required – is a function of the pump design and is the lowest value of NPSH at which the pump can be guaranteed to operate without significant cavitation. There is no absolute criterion for determining what this minimum allowable NPSH should be, but pump manufacturers normally select an arbitrary drop in total dynamic head (differential head) of 3% as the normal value for determining NPSHr. |
| NPSHa | NPSH available – is a function of the system in which the pump operates and is equal to the absolute pressure head on the liquid surface plus the static liquid level above the pump centreline (negative for a suction lift) minus the absolute liquid vapour pressure head at pumping temperature minus the suction friction head losses. |
| Cavitation | Process in which small bubbles are formed and implode violently; occurs when NPSHa < NPSHr |
| Density | (specific weight of a fluid) – Weight per unit volume, often expressed as pounds per cubic foot or grams per cubic centimetre. |
| Flooded Suction | Liquid flows to pump inlet from an elevated source by means of gravity |
| Flow | A measure of the liquid volume capacity of a pump. Given in gallons per minute (GPM), litres per second and cubic metres per hour. |
| Head | A measure of pressure, expressed in metres for centrifugal pumps. Indicates the height of a column of water being moved by the pump (without friction losses). |
| Pressure | The force exerted on the walls of a tank, pipe, etc. by a liquid. Normally measured in pounds per square inch (psi) or kilopascals ( kpa). |
| Prime | Charge of liquid required to begin pumping action when liquid source is lower than pump. Held in pump by a foot valve on the intake line or by a valve or chamber within the pump. |
| Self/Dry Priming | Pumps that draw liquid up from below pump inlet (suction lift), as opposed to pumps requiring flooded suction. |
| Specific Gravity | The ratio of the weight of a given volume of liquid to pure water. Pumping heavy liquids (specific gravity greater than 1.0) will require more drive kilowatts. |
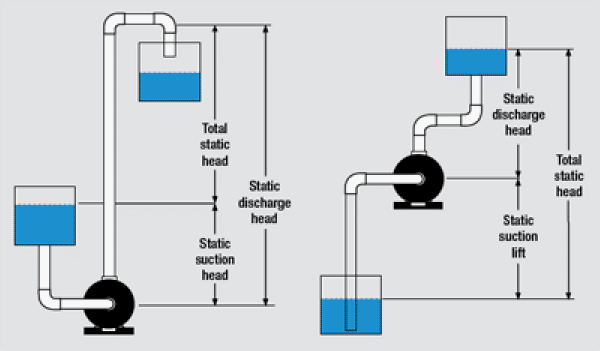
| Static Discharge Head | Maximum vertical distance (in metres) from pump to point of discharge with no flow |
| Strainer | A device installed in the inlet of a pump to prevent foreign particles from damaging the internal parts. |
| Sump | A well or pit in which liquids collect below floor level; sometimes refers to an oil or water reservoir. |
| Total Head | Sum of discharge head, suction lift, and friction loss. |
| Viscosity | The “thickness” of a liquid or its ability to flow. Most liquids decrease in viscosity and flow more easily as they get warmer. |
| Valves | |
| Bypass Valve | Internal to many pump heads that allow fluid to be recalculated if a given pressure limit is exceeded. |
| Check Valve | Allows liquid to flow in one direction only. Generally used in discharge line to prevent reverse flow. |
| Foot Valve | A type of check valve with a built-in strainer. Used at point of liquid intake to retain liquid in system, preventing loss of prime when liquid source is lower than pump. |
| Relief Valve | Used at the discharge of a positive displacement pump. An adjustable, spring loaded valve opens when a preset pressure is reached. Used to prevent excessive pressure build up that could damage the pump or motor. |
Friction Head – The loss in pressure or energy due to frictional losses in flow.
Discharge Head – The outlet pressure of a pump in operation.
Total Head – The total pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of a pump in operation.
Suction Head – The inlet pressure of a pump when above atmospheric pressure.
Suction Lift – The inlet pressure of a pump when below atmospheric pressure.