| |
| Bearings are classified as plain journal or
antifriction bearings. An antifriction bearing is a
bearing that contains moving elements to provide a
low friction support surface for rotating or sliding
surfaces. Antifriction bearings are commonly made
with hardened rolling elements (balls and rollers)
and races. |
| |
| Working principal of friction
bearing |
|
Video |
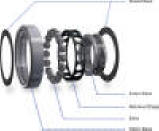
| Anti friction bearings consist of the following
basic elements.
|
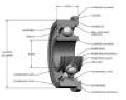
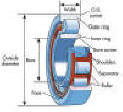
| The races or rings |
In the case of ball bearings, the bearing has inner and
outer races and a set of balls. Each race is a ring with a
groove where the balls rest. The groove is usually shaped so
the ball is a slightly loose fit in the groove. Thus, in
principle, the ball contacts each race at a single point. |
| |
|
In the case of roller bearings, the bearing has inner and
outer races and a set of rollers. Each race is a ring with a
groove where the rollers rest. The groove is usually shaped
so the roller is a slightly loose fit in the groove. Thus,
in principle, the roller contacts each race at a line
contact point. |
| |
| The rolling element |
|
The rolling element is determined by the magnitude of the
load and direction of the load (axial or radial). |
| |
|

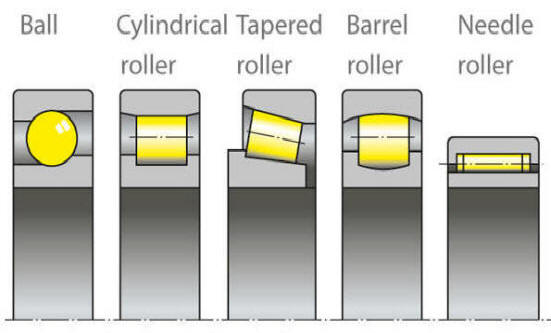
Ball
Balls are point contact. Most
commonly used rolling element. Relative large radial
loads with some axial loads. |

Roller
Rollers are line contact and thus
can carry very large radial loads with minimal axial
loads. |
|

Taper roller
Taper rollers are line contact and
will run in taper races. They can carry both
radial and axial loads. |

Needle roller
Needle rollers is similar to
rollers, their length is longer in relation to their
diameter. They can be used with races or
without. Normally used where radial space is
limited |
|

Spherical roller
(Barrel)
A spherical roller bearing is a
rolling-element bearing that permits rotation with
low friction, and permits angular misalignment.
Typically these bearings support a rotating shaft in
the bore of the inner ring that may be misaligned in
respect to the outer ring. |
 |
|
|
|
|
Cage or retainer |
|
The ball bearing cage (also known as a ball bearing retainer
or ball separator – these are used interchangeably), is the
component in a ball bearing that separates the balls,
maintains the balls and rollers symmetrical radial spacing,
and in most cases, holds the bearings together. Solid
cages consist of brass, steel, light metal, sinter iron and
phenolic. Manufacture process for metal and phenolic cages
is consisting of turning and milling. Cages made out of
plastic materials are manufactured by injection moulding.
|
Press metal cage |
Machined cage |

Nylon cage |
|
|
|
|
Bearing
seals |
The primary functions of a bearing seal are to keep
lubricant in the bearing and bearing chamber contaminants
out. Bearings are pre-pact with grease in the factory
and will stay lubricated for the life of the bearing.
Some seals are integral to the bearing; others aren’t. The
focus here is on what to consider when selecting external
bearing seals. Key factors in making the right choice for an
application typically include:
- Bearing type (rolling or sleeve)
- Lubricant (oil or grease)
- Seal friction and consequent heating
- Shaft surface speed and finish
- Physical space available
|
|
Nylon seal |

Metal seal |

Rubber seal |
|
|
|
|
Type of anti friction bearings
|
|
|
|
|
|
|